Sensorless Current Mode Control to Stabilize an Input-Series-Output- Parallel Converter
Jonathan Kimball with adviser Philip T. Krein
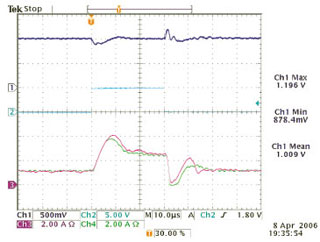
Figure 42: Response to a load step. Output voltage (channel 1, 500 mV/div), load step command (channel 2, 5 V/div), phase 5 inductor current (channel 3, 2 A/div), and phase 1 inductor current (channel 4, 2 A/div).
Many solutions have been proposed for power converters with high conversion ratios. The performance and efficiency of nonisolated converters degrades significantly when the ratio between input and output voltage exceeds 4:1. Isolated converters can operate with an arbitrary ratio by changing a transformer turns ratio, but higher turns ratios yield lower efficiency. The input-series-outputparallel (ISOP) topology uses several isolated converters, each with a low transformer turns ratio, connected so that they equally share input voltage and output current.
Previous control schemes for the ISOP topology are complicated and sacrifice performance. This project used a modified sensorless current mode (SCM) controller to force the converters to share input voltage equally. Stability has been shown analytically. The method was demonstrated experimentally on a five-phase converter with an overall conversion ratio of 30:1 (see Figure 42).
As part of this project, SCM modeling methodology was extended to a multiphase system (see Figure 43). A model composed of a standard SCM model multiplied by a comb filter matches experimental results well enough for feedback design. This technique is appropriate for any multiphase SCM controller.
