A Global Maximum Power Point Tracking Method for PV Module-Integrated Converters
Sairaj Dhople with adviser A. Domínguez-García
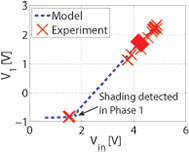
Figure 19: Negative by-pass diode voltage indicates partial shading.
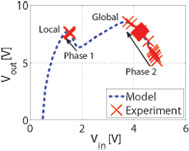
This work proposes a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) method to seek the global MPP in PV modules. The method infers partial shading—and hence the possibility of multiple maxima—by monitoring bypass-diode voltages and initiating a global search routine only if a bypass diode turns on. Under nominal conditions, conventional MPPT is implemented through a perturbation-based approach. Our technique provides a significant advantage over existing methods that periodically scan the entire PV power profile. Experimental results have demonstrated that the algorithm can track the global MPP for sub-module and cell-level shading scenarios. For example, Figure 18 depicts the performance of the algorithm for sub-module shading of a PV module. In Phase 1, a conventional MPP algorithm seeks the local maximum. By detecting a negative bypass-diode voltage (Figure 19), we infer partial shading, and in Phase 2, the controller seeks the global maximum. This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation under grant ECCS-CAR-0954420 and the Grainger Center for Electric Machines and Electromechanics.
This research is funded by the Grainger Center for Electric Machinery and Electromechanics.